Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 3D Display Components Support Center, Gumi Electronics and Information Technology Research Institute, Gumi-si, Gyeongsangbuk-do 730-853, Korea
2 School of Electronics Engineering, College of IT Engineering, Kyungpook National University, Daegu 702-701, Korea
3 Department of Electrical, Electronic, and Control Engineering, IITC, Hankyong National University, 327 Chungang-ro, Anseong-si, Gyonggi-do 456-749, Korea
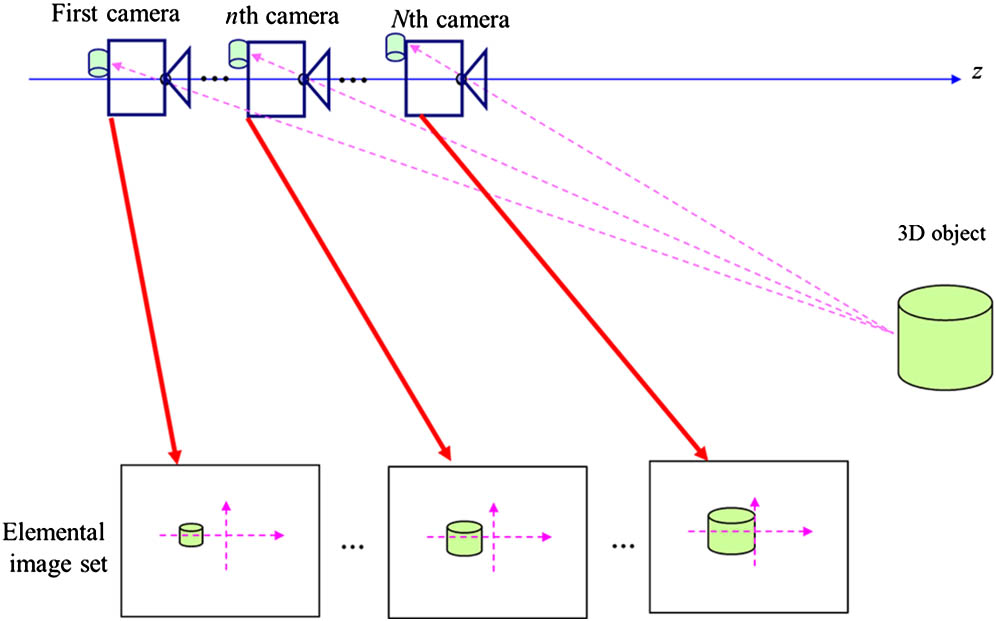
In this Letter, we propose a three-dimensional (3D) free view reconstruction technique in axially distributed image sensing (ADS). In typical integral imaging, free view reconstructed images can be obtained by tilting all elemental images or tilting the reconstruction plane due to large lateral perspectives for 3D objects. In conventional ADS, the reconstructed images at only a front view can be generated since the sensor is moved along with its optical axis so that it has small lateral perspectives for 3D objects. However, the reconstructed 3D images at any viewing point may be obtained because the virtual viewing camera may capture these slightly different perspectives for 3D objects. Therefore, in this Letter, we employ the virtual viewing camera to visualize the 3D images at the arbitrary viewing point. To support our proposed method, we show the experimental results.
110.0110 Imaging systems Chinese Optics Letters
2017, 15(8): 081102

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Department of Computer Science and Electronics, Kyushu Institute of Technology, Fukuoka 820-8502, Japan
2 Department of Electrical Energy and Computer Engineering, Gyeongju University, 188 Taejongro, Gyeongju City, KyeongsangBukdo, 38065, Republic of South Korea
3 Department of Electrical, Electronic, and Control Engineering, IITC, Hankyong National University, 327 Chungang-ro, Anseong-si, Gyonggi-do 456-749, Republic of South Korea
In this Letter, we propose an elemental image regeneration method of three-dimensional (3D) integral imaging for occluded objects using a plenoptic camera. In conventional occlusion removal techniques, the information of the occlusion layers may be lost. Thus, elemental images have cracked parts, so the visual quality of the reconstructed 3D image is degraded. However, these cracked parts can be interpolated from adjacent elemental images. Therefore, in this Letter, we try to improve the visual quality of reconstructed 3D images by interpolating and regenerating virtual elemental images with adjacent elemental images after removing the occlusion layers. To prove our proposed method, we carry out optical experiments and calculate performance metrics such as the mean square error (MSE) and the peak signal-to-noise ratio (PSNR).
110.0110 Imaging systems 110.6880 Three-dimensional image acquisition Chinese Optics Letters
2016, 14(12): 121101
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Department of Optometry, Eulji University, 553, Sanseong-daero, Sujeong-gu, Seongnam-si, Gyonggi-do, South Korea
2 Department of Electrical, Electronic, and Control Engineering, Hankyong National University, Kyonggi-do 456-749, South Korea
We propose a novel method of slice image reconstruction with controllable spatial filtering by using the correlation of periodic delta-function arrays (PDFAs) with elemental images in computational integral imaging. The multiple PDFAs, whose spatial periods correspond to object’s depths with the elemental image array (EIA), can generate a set of spatially filtered EIAs for multiple object depths compared with the conventional method for the depth of a single object. We analyze a controllable spatial filtering effect by the proposed method. To show the feasibility of the proposed method, we carry out preliminary experiments for multiple objects and present the results.
110.6880 Three-dimensional image acquisition 110.4190 Multiple imaging Chinese Optics Letters
2015, 13(3): 031101

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Department of Electric, Electronic, and Control Engineering, Hankyong National University, Kyonggi-do 456-749, South Korea
2 Institute of Ambient Intelligence, Dongseo University, Churye-ro, Sasang-Gu, Busan 617-716, South Korea
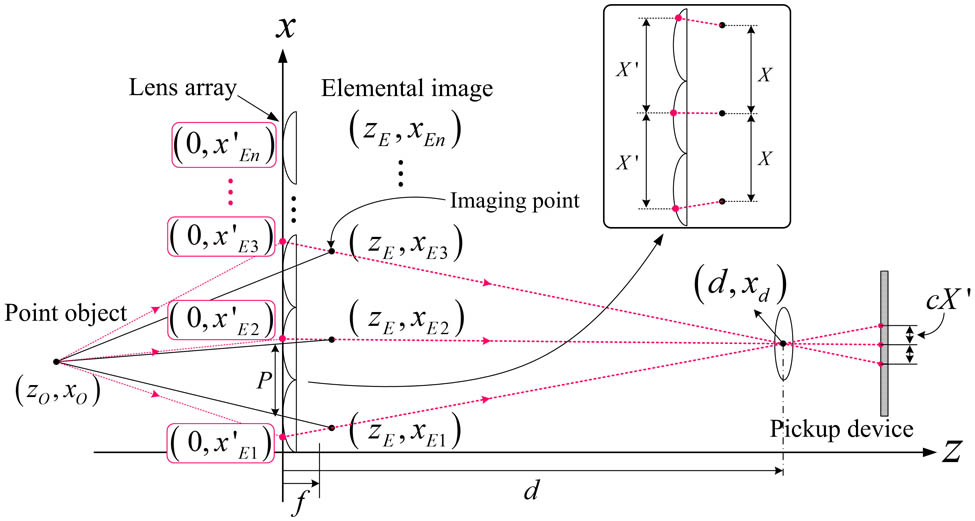
In this Letter, we propose a three-dimensional (3D) image reconstruction method with a controllable overlapping number of elemental images in computational integral imaging. The proposed method can control the overlapping number of pixels coming from the elemental images by using the subpixel distance based on ray optics between a 3D object and an image sensor. The use of a controllable overlapping number enables us to provide an improved 3D image visualization by controlling the inter-pixel interference within the reconstructed pixels. To find the optimal overlapping number, we simulate the pickup and reconstruction processes and utilize the numerical reconstruction results using a peak signal-to-noise ratio (PSNR) metric. To demonstrate the feasibility of our work in optical experiments, we carry out the preliminary experiments and present the results.
110.0110 Imaging systems 110.6880 Three-dimensional image acquisition Chinese Optics Letters
2015, 13(5): 051101

Author Affiliations
Abstract
Department of Electrical, Electronic, and Control Engineering, Institute of Information Technology Convergence, Hankyong National University, 327 Chungang-ro, Anseong-si, Kyonggi-do 456-749, Korea
In this Letter, we propose a novel three-dimensional (3D) color microscopy for microorganisms under photon-starved conditions using photon counting integral imaging and Bayesian estimation with adaptive priori information. In photon counting integral imaging, 3D images can be visualized using maximum likelihood estimation (MLE). However, since MLE does not consider a priori information of objects, the visual quality of 3D images may not be accurate. In addition, the only grayscale image can be reconstructed. Therefore, to enhance the visual quality of 3D images, we propose photon counting microscopy using maximum a posteriori with adaptive priori information. In addition, we consider a wavelength of each basic color channel to reconstruct 3D color images. To verify our proposed method, we carry out optical experiments.
030.5260 Photon counting 100.6890 Three-dimensional image processing 110.6880 Three-dimensional image acquisition 170.6900 Three-dimensional microscopy Chinese Optics Letters
2015, 13(7): 070301
Author Affiliations
Abstract
Department of Electrical, Electronic and Control Engineering, Hankyong National University, Anseong 456-749, Korea
We propose a security-enhanced double-random phase encryption (DRPE) scheme using orthogonally encoded image and electronically synthesized key data to cope with the security problem of DRPE technique caused by fixed double-random phase masks for encryption. In the proposed scheme, we adopt the electronically synthesized key to frequently update the phase mask using a spatial light modulator, and also employ the orthogonal encoding technique to encode the image and electronically synthesized key data, which can enhance the security of both data. We provide detailed procedures for encryption and decryption of the proposed scheme, and provide the simulation results to show the encryption effects of the proposed scheme.
060.4785 Optical security and encryption 200.4560 Optical data processing Chinese Optics Letters
2015, 13(1): 010603





